AC Circuits - Basic Terminologies
Basic Terminologies in AC circuits
Alternating current (AC):
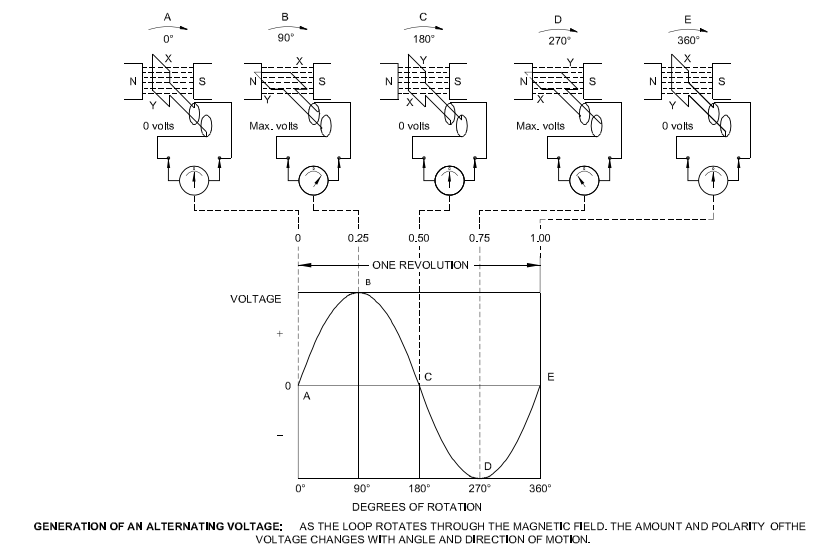
An alternating current (AC) circuit is one in which the direction and amplitude of the current flow change at regular intervals with respect to time.
Frequency (F): The frequency of an AC sine wave is the number of cycles produced per second. unit of frequency is the hertz (Hz).
Instantaneous value: The value of an alternating quantity at any particular instant is called instantaneous value.
The instantaneous values of a sine wave voltage is shown in above Fig. It is 3.1 volts at 1μs.
Peak value or maximum value (Vm/Vp): The peak value of a sine wave refers to the maximum voltage or current value.
Peak-to-peak value (Vpp):
The peak-to-peak value of a sine wave refers to its total overall value from one peak to the other. It is equal to two times the peak value.as shown in above fig.
Effective value: The effective value of an alternating current is that value which will produce the same heating effect as a specific value of a steady direct current.
effective value of an alternating current or voltage is also Known as root mean square (rms) value.
effective value/RMS Value of a sine wave of current or Voltage is always equal to 0.707 times its peak value.
e.g. for voltage, V = 0.707 Vm
for current, I = 0.707 Im
Average value:
Find the area covered by the curve over the horizontal axis, then divide that area by the base horizontal length. Or Simply we can say that,
average value is equal to 0.637 times the maximum value for sine wave-form
e.g. for voltage, Vav = 0.637 Vm
for current,Iav = 0.637Im
Form factor (Kf ):
Form factor is defined as the ratio of effective value to average value of half cycle.
For sinusoidal AC
Kf = 0.707 Im/ 0.637 Im = 1.11
Advantages of AC over DC:
1. AC voltages can be raised or lowered with ease. This makes it ideal for transmission purposes.
2. Large amounts of power can be transmitted at high voltage and low currents with minimum loss.
3. Because the current is low, smaller transmission wires can be used to reduce installation and maintenance costs. And Also,
- AC is easy to generate than DC.
- It is cheaper to generate AC than DC.
- AC generators take higher efficiency than DC.
- The loss of energy during transmission in negligible for AC in long distance.
- The AC can be easily converted to DC. • It can easily stepup or stepdown using transformer.
- The value or magnitude of AC can be decreased easily without loss of excess of energy using choke.





Comments
Post a Comment
thanks for comment